Scalable Neural Indoor Scene Rendering
SIGGRAPH 2022 (Journal track)
Xiuchao Wu1* Jiamin Xu1* Zihan Zhu1 Hujun Bao1 Qixing Huang2 James Tompkin3 Weiwei Xu1
*joint first authors
1Zhejiang University 2University of Texas at Austin 3Brown University

Abstract
We propose a scalable neural scene reconstruction and rendering method to support distributed training and interactive rendering of large indoor scenes. Our representation is based on tiles and a separation of view-independent appearance (diffuse color and shading) and view-dependent appearance (specular highlights, reflections), each of which predicted by lower-capacity MLPs. After assigning MPLs per tile, our scheme allows tile MLPs to be trained in parallel and still represent complex reflections through a two-pass training strategy. This is enabled by a background sampling strategy that can augment tile information from a proxy global mesh geometry and tolerate typical errors from reconstructed proxy geometry. Further, we design a two-MLP based representation at each tile to leverage the phenomena that view-dependent surface effects can be attributed to a reflected virtual light at the total ray distance to the source. This lets us handle sparse samplings of the input scene where reflection highlights do not always appear consistently in input images. We show interactive free-viewpoint rendering results from five scenes. One of them covers areas of more than 100 ㎡. Experimental results show that our method produces higher-quality renderings than a single large-capacity MLP and other recent baseline methods.
Rendering Results





Method
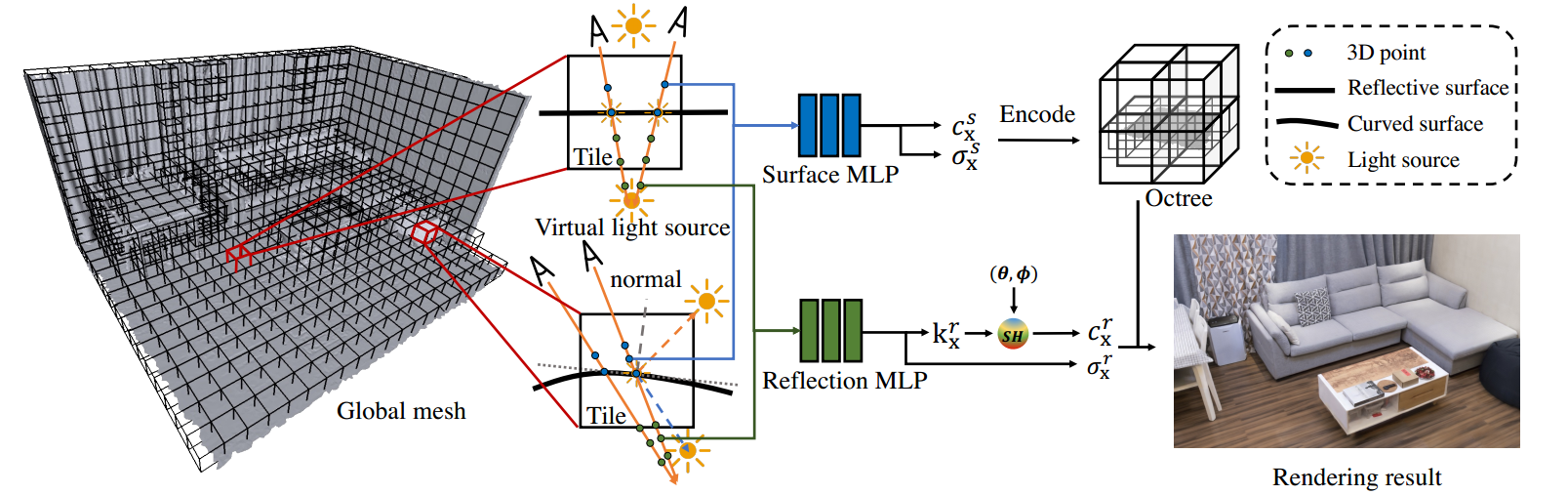
We create tiles over the volumetric scene and optimize per-tile MLPs. Each tile has two MLPs: 1) The surface MLP that encodes density and view independent color, which is later stored in an octree for fast rendering. 2) The reflection MLP that encodes view-dependent effects like highlights using virtual points underneath the surface at the ray distance of the reflected light. Color outputs from both paths are combined in the final rendering.
Explainer Video
Distributed Training
Our scheme allows tile MLPs to be trained in parallel.
Interactive Rendering
The rendering time for a frame of resolution is 50ms on average.
Comparisons
Our method shows improved rendering results for specular reflection and temporal coherence over baselines
Extrapolation
We test the case when novel viewpoints are far from captured views.
Simple Editing
Full Video
BibTex
@article{wu2022snisr,
title={Scalable Neural Indoor Scene Rendering},
author={Wu, Xiuchao and Xu, Jiamin and Zhu, Zihan and Bao, Hujun and Huang, Qixing and Tompkin, James and Xu, Weiwei},
journal={ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG)},
year={2022}
}
Acknowledgements
Supported by Information Technology Center and State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University.